| Properties | Details |
|---|---|
| SFDA Classification | Class IIb |
| Purpose of Use | A computerized tomography x-ray machine is a diagnostic and follow-up device that produces high-volume images of the interior of the body, by shining x-rays from a source that is attached to a ring around the body. The data from the X-ray detectors in the ring is processed and two-dimensional cross-sections are formed. These slices can also be combined to make a 3D model. |
| Work Location & End-User | Work Location: In the radiology department of the hospital. End User: A radiologist or technician who specializes in a computerized tomography (CT) scan. |
| Parts & Accessories | Basic parts: 1- Movable diagnostic table. 2- Ring of the imaging device: Generator: supplies the circuit with power. It contains an x-ray source tube. - Digital X-ray detectors or receivers installed in the inner surface of the ring opposite the X-ray tube. - Anti-scattered rays "Collimator": absorbs the scattered rays from the main rays emitted from the tube to allow the receivers to absorb the remaining main rays. The anti-scattered radiation is made of tungsten or lead, and is placed in the shafts between the pickups. Slip Ring Technology: It is a technology that relies on carbon brushes in the stator of the ring and a conductive metal surface in the rotor. This technology is useful in transmitting data from the receivers and control buttons to the computer, as well as supplying the loop with power. This technology eliminates the need for wires to connect because the wires will be twisted and damaged immediately once the loop is rotated. Filters: They remove weak rays that are known to be completely absorbed by the body. These filters protect the body from excessive rays and improve image quality. 3- The device's computer in the control room: The control room inside the device room shall be isolated and protected by walls of lead-equivalent glass. 4- Contrast agent: It is a substance that has the ability to absorb a large amount of X-rays, so they appear clearly in the imaging. This material must be safe for the body. It is used to improve the parameters of the internal organ to be imaged, which does not absorb X-rays as much as the internal tissues. Agent synthesized from iodine is used for imaging the circulatory system, while an agent made from barium is used for imaging the digestive system. 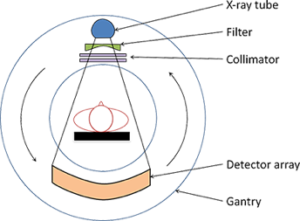 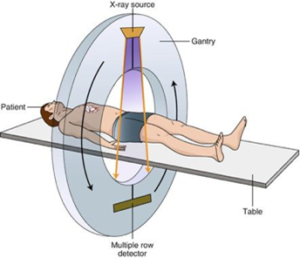 |
| Operation | 1- After the patient lies on the movable diagnostic table, the table slowly moves into the ring. 2- During the movement of the table, the tube emits x-rays toward the body to the digital x-ray pickups. The ring also rotates around the body, giving a full view of the body, creating a cross-section of the body. 3- The antennas measure the amount of radiation after part of it is absorbed by parts of the body. It picks up the rest of the x-rays and transmits the signal to the computer. 4- Using image processing techniques, the computer generates a two-dimensional image for each turn of the ring (slice) with a thickness of approximately 1 to 10 mm. The image is then stored in the computer. 5- After reaching the desired number of images (slices), the computer collects these images to form a three-dimensional stereotype showing the skeleton, internal organs, and tissues. 6- The device emits high heat while it is working. Therefore, it is necessary to have a cooling system in the device. Some types rely on air cooling, and others rely on water cooling. |
| Common Problems | 1- A beeping sound while the loop is spinning. This sound indicates a problem with the installation of the X-ray tube. The bearings, or the tube itself may be worn out and need replacing. 2- If the ring continues to rotate after the imaging is completed, this is also a sign of a problem with the installation of the x-ray tube. 3- If the diagnostic table does not move well or at all, the problem is with the motor. Confirm the problem and fix it or replace the motor when needed. 4- If the cooling time is excessively long, it means that the cooling system has a malfunction. It should be checked by a professional engineer. If an "Arc error" message appears, this means that there is a so-called electrical arcing in the ray tube. If the message appears with the device stopped during shooting, this problem can be removed by the computer itself. Go to the alerts page on the computer and remove the problem. If the device turns off with the appearance of the message, this means that the problem occurs continuously and that there is a problem with the x-ray tube. You should give the tube time to warm up if it is cold and not start shooting when it is cold. |
| Manufacturers | • Philips • GE Healthcare • Siemens • Canon • Toshiba |
| Sources | • Saudi Food and Drug Authority • National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering • Radiopaedia • Nuclear Fields • Radclass • US Food and Drug Administration • TECHNICAL PROSPECTS • PRIZME |
