| Properties | Details |
|---|---|
| SFDA Classification | Class IIa |
| Purpose of Use | It has diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. As a diagnostic instrument, it provides the ability to show the inside of the human body or take biopsy through inserting a flexible tube from the natural opening, e.g., nostrils, anus, mouth, urethra, and vagina, or a small incision. It can also deliver therapeutic materials to the targeted area.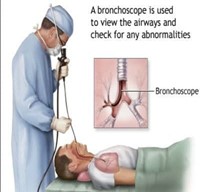 |
| Work Location & End-User | Location: Since there are many types of the endoscope, a separate department is set for them all, called Endoscopy department. End-user: Doctors who are specialized in different area of endoscopy (Gastroenterologists) and nurses. |
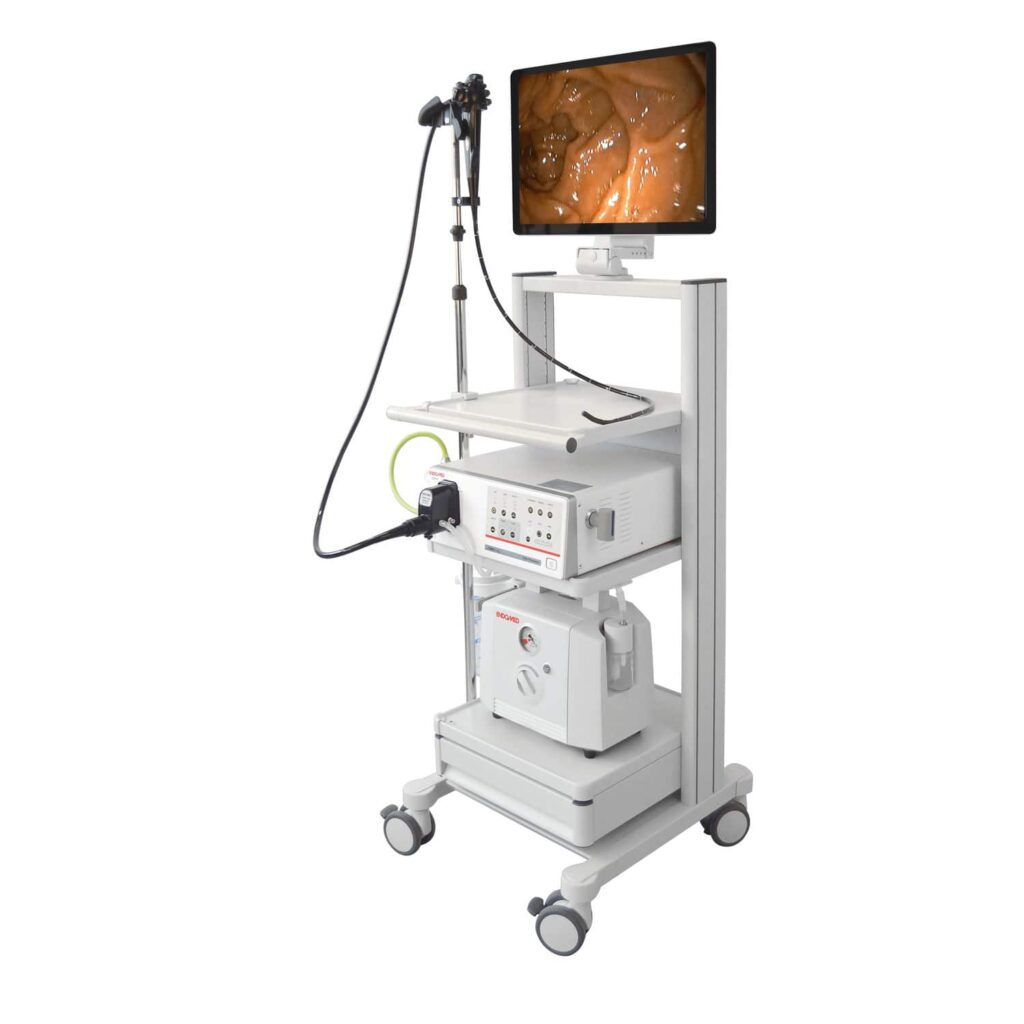
| Parts & Accessories | Essential of the system: 1-Light source with an intensity that can be controlled. 2- Video processor: receive and process the signals from the CCD-CMOS. 3- Monitor screen: show the live video and the patient’s information, control the settings, and save the data. 4- Trolley. Main parts of the endoscope: 1- Connector section: • Light guide connector that connects to the light source. It also offers connections to air/water tank, leakage tester, suction, and electrical contacts. • Light guide tube which is a link between the light guide connector and the control section of the endoscope. 2- Operation Section Assembly (OSA) or Control section: • Control knobs that allow the change of the angle of the tube’s end in the vertically and/or horizontally. They can be locked to a fixed angle. • Air/water valve which controls the flow of air and water. • Suction valve. • Programmable buttons to record videos, take photos and save the data. The command of each button can be specified in the settings. 3- Insertion Section Assembly (ISA): • Insertion tube. • Bending section, which is the part that is controlled by the control knobs. The distal end (terminal): It is the end of the tube and it contains several important elements: • Camera: its lens takes signals and sends them to the processor. • Light guide lens. • Air/water nozzle to clean the camera. • Water jet opening connected to a water pump in order to continuously wash the camera for certain cases such as bleeding. • Biopsy channel opening. Accessories: • Video recorder. • printer. |
| Operation | 1- The light source lights up the area around the distal end of the endoscope through the optic fibers. 2- The objective lens of the CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera in the distal end gathers the reflected light as signals and send them to the processor. 3- The processor reads and process the signals and shows them as a photo in the screen. 4- During this process, the water-air valve must be used to flush the camera and the suction valve for excess fluid. 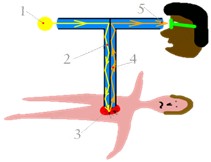 |
| Common Problems | The most common problems: 1. If there is a superficial scratch on the camera lens, it can be cleansed and fixed. Whereas if the scratch is deep, it is better to replace the camera. 2. If the light window is broken, change the objective lens. 3. If the cap surface is scratched or broken, replace it with a new one. 4. If the rubber has bends, cut or torn, replace it with a new one.    |
| Manufacturers | • Karl Storz • Olympus • FujiFilm • Pentax Medical |
| Sources | • Saudi Food and Drug Authority • Merriam-Webster • MedicineNet • Highgate Hospital • Radiology Key • Partners For Endoscopy • Steris Animal Health US • Abdominal Key • Springer • Moqatel • Explain that Stuff • Etherealmind • Fujifilm • Olympus • Pentax Medical • Stryker |
